Pine nuts are one of the lesser known nut varieties, but they have been increasing in popularity over recent years.
These nuts have a tasty, buttery flavor and they work well as a snack and provide a delicious flavor when used in cooking.
This article examines their nutrition profile and the potential health benefits (and drawbacks) they offer.
Are pine nuts good for you?
WHAT ARE PINE NUTS?
A hard shell surrounds these nuts, and this shell is enclosed within a pine cone. We can see the actual nuts themselves in the above image.
Asia dominates the global production of pine nuts, which are also known as pignoli/pinoli.
Surprisingly, North Korea is the number one producer.
Other countries producing large amounts of pine nuts include Russia, China, Pakistan, and Afghanistan (1).
Pine nuts also grow around the world, including in Europe and the United States.
The nuts have a mild flavor, and a nutty, and slightly sweet, buttery taste.
For this reason, they are a valued ingredient in cooking, and they are one of the main ingredients in pesto sauce.
Although there are dozens of pine tree varieties, only a small number are capable of growing seeds (pine nuts) big enough to eat.
The most popular species for commercial production of pine nuts include;
- Korean Pine (Pinus Koraiensis)
- Mexican Pinyon (Pinus Cembroides)
- Chilgoza Pine (Pinus Gerardiana)
Nutritionally, pine nuts have a lot to offer, and they are a rich source of nutrients.
Calories and Macros
| Calories/Macronutrient | Per oz (28 g) Serving | Per 100 g |
| Calories | 188 kcal | 673 kcal |
| Carbohydrate | 3.7 g | 13.1 g |
| – Fiber | 1.0 g | 3.7 g |
| – Sugar | 1.0 g | 3.6 g |
| Fat | 19.2 g | 68.4 g |
| Saturated Fat | 1.4 g | 4.9 g |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 5.3 g | 18.8 g |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | 9.5 g | 34.1 g |
| – Omega-3 | 31.4 mg | 112 mg |
| – Omega-6 | 9410 mg | 33606 mg |
| Protein | 3.8 g | 13.7 g |
Pine nuts are primarily a source of (polyunsaturated) fat, and they also contain moderate amounts of carbohydrate and protein.
Vitamins
| Calories/Macronutrient | Per oz (28 g) Serving | Per 100 g |
| Vitamin K1 | 19% RDI | 67% RDI |
| Vitamin E | 13% RDI | 47% RDI |
| Vitamin B1 | 7% RDI | 24% RDI |
| Vitamin B3 | 6% RDI | 22% RDI |
| Vitamin B2 | 4% RDI | 13% RDI |
| Folate | 2% RDI | 8% RDI |
| Vitamin B6 | 1% RDI | 5% RDI |
| Vitamin B5 | 1 % RDI | 3% RDI |
| Vitamin A | Trace | 1% RDI |
| Vitamin C | Trace | 1% RDI |
As the table demonstrates, pine nuts are an excellent source of vitamin K1 and a rare dietary source of vitamin E.
Minerals
| Calories/Macronutrient | Per oz (28 g) Serving | Per 100 g |
| Manganese | 123% RDI | 440% RDI |
| Copper | 18% RDI | 66% RDI |
| Magnesium | 18% RDI | 63% RDI |
| Phosphorus | 16% RDI | 57% RDI |
| Zinc | 12% RDI | 43% RDI |
| Iron | 9% RDI | 31% RDI |
| Potassium | 5% RDI | 17% RDI |
| Calcium | 1 % RDI | 2% RDI |
| Selenium | Trace | 1% RDI |
| Sodium | Trace | Trace |
Pine nuts are very high in manganese, copper, magnesium and phosphorus.
Aside from this, they contain most other essential minerals in small to moderate amounts.
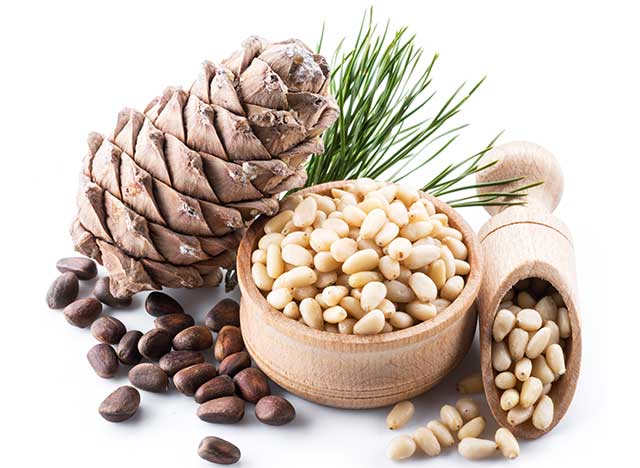

Owing to their impressive nutrient profile, pine nuts have several benefits.
1) Significant Source of Vitamin EIt can be quite difficult to find food sources of vitamin E, and nuts and seeds are one of the major providers.
Pine nuts are a particularly good source of the vitamin, and they contain 2.6 mg of vitamin E per ounce (28-gram) serving. This amount works out at 13% of the RDI for the vitamin (2).
Vitamin E plays numerous vital roles within the body.
Among these roles, vitamin E is well known for its antioxidant function, and the vitamin helps to inhibit damage caused by free radical reactions within the body (3).
Studies also show that vitamin E can stimulate and boost the immune response (4, 5).
2) Pine Nuts Are a Substantial Source of Manganese
Pine nuts offer one of the most concentrated sources of manganese in the world.
Since 100 grams of the nuts provides over 400% of the RDI for manganese, just a small one-ounce handful offers 123% of the RDI.
Manganese plays an essential role in the skeletal system, and alongside support minerals like calcium, copper, magnesium, and zinc, it can help to strengthen bones and improve bone mass density (6, 7).
Sufficient intake of manganese is also necessary for prolidase activation, an enzyme that assists with wound healing (8).
3) May Help To Boost Satiety
One of the biggest keys to satiety is consuming enough protein, which is widely regarded to be the most satiating macronutrient (9, 10).
Other than that, lifestyle factors like sufficient sleep and general happiness/mood also play a role (11, 12).
Due to early in-vitro (taking part outside a living creature) trials, researchers previously thought that triacylglycerols from pine nuts might offer some unique satiating benefits above and beyond this.
Although promotion of this belief persists, randomized studies in human participants have shown this not to be the case.
In a randomized controlled trial, pine nut triacylglycerols had no significant effect on appetite suppression or energy intake (13).
However, choosing pine nuts as a snack (especially in replacement of common high-sugar options) may help with satiety due to the protein, fiber, and micronutrient profile of the nuts.
4) Rich In B Vitamins

Pine nuts are a decent source of B vitamins, and they contain a reasonably high amount of vitamins B1 and B3.
Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) is essential for converting the food we eat into energy that we can use, muscular contraction, and nerve signaling (14).
Similar to vitamin B1, B3 (Niacin) also plays a role in the conversion of food into energy.
Additionally, some studies suggest that vitamin B3 may have photoprotective properties.
In plain English, this means that the vitamin may help to protect the skin against UV-induced damage (15).
The vitamin B1 and B3 content of pine nuts is 24% and 22% of the RDI respectively.
5) Pine Nuts Are Relatively High In Protein
Almonds and pistachio nuts are the kings of protein among nuts.
However, pine nuts also offer a good source of protein, and they provide nearly four grams per one-ounce (28-gram) serving.
Per 100 grams, pine nuts supply 13.7 grams of protein, which is much higher than nuts like macadamia or pecans (2).
6) A Source of Caffeic Acid
Pine nuts are a source of polyphenols; specifically, the compound they contain in the highest amount is called caffeic acid (16, 17).
Caffeic acid is also found in coffee, and it is one of the more bioavailable polyphenols. One recent randomized controlled trial found that consuming dietary sources of caffeic acid increases the plasma concentration of the compound (18, 19).
Various studies suggest that caffeic acid is capable of exerting anti-inflammatory effects. However, more research from human trials is necessary. (20, 21, 22).
However, if this compound is of particular interest, sources such as coffee, red wine, and olive oil are more concentrated options.
Like all foods, there are some potential drawbacks to consuming pine nuts.
1) Pine Nut Allergy
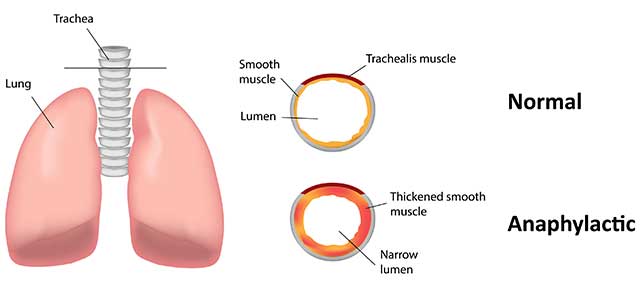
Similar to other nuts, pine nuts may also cause allergic reactions in some individuals.
Pine nuts contain a major protein allergen known as ‘Pin p 1,’ and the nuts can cause a range of allergic responses, causing symptoms that range from mild to severe (23, 24, 25).
In a worst-case scenario, pine nuts have been known to cause anaphylaxis (anaphylactic shock), a potentially life-threatening allergic response (26).
2) “Pine Nut Syndrome”
Pine nuts have been known to cause some strange—but not dangerous—side effects in some people.
The term ‘pine nut syndrome’ (or sometimes ‘pine mouth syndrome’) is used to describe these effects.
These side effects revolve around an extremely bitter aftertaste that can last for days (or even weeks) after eating the nuts.
Although the mechanisms which cause pine mouth syndrome are currently not fully understood, it appears that one specific species of pine nut (Pinus armandii – ‘Chinese white pine’) can contain a toxin which causes the condition (27, 28).
Pine nut syndrome usually kicks in within 12 to 48 hours after eating pine nuts (29).
Pine nuts add a lot of flavor to food, and it is easy to use them; add a handful to any dish.
Some people prefer to lightly toast pine nuts before cooking, as this deepens their flavor and adds even more taste to dishes.
For some ideas, there is a wide range of pine nut recipes here.
FINAL THOUGHTSPine nuts are a nutrient-dense nut that offers a delicious nutty and buttery flavor.
The nuts are rich in vitamins and minerals, provide a decent amount of protein, and they can upgrade the taste of various dishes.
For more on nuts, see this complete guide to pecans.
By:
Michael Joseph / Nutrition Advance.

Hello
I was googling for content about pine nuts When I came across your excellent resource page.
I just wanted to say that your page helped me, I would have found the excellent resource.
Here it is in case you’d like to check it out https://www.elnodiacademy.com/pine-nuts-benefits
Also, my guide might make a nice addition to your page.
Either way, thanks for putting together your list of resources. Have a great day.